New research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has revealed that training one arm can improve strength and decrease muscle loss in the other arm -- without even moving it. The findings could help to address the muscle wastage and loss... Continue Reading →
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered a new inflammatory disorder called vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, autoinflammatory and somatic syndrome (VEXAS), which is caused by mutations in the UBA1 gene. VEXAS causes symptoms that included blood clots... Continue Reading →
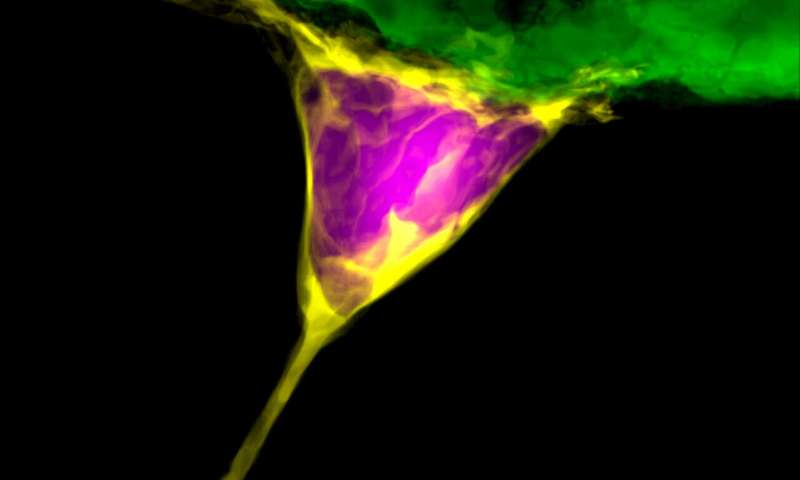
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) -- nanometer sized messengers that travel between cells to deliver cues and cargo -- are promising tools for the next generation of therapies for everything from autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases to cancer and tissue injury. EVs derived... Continue Reading →
A new mechanism of blood redistribution that is essential for the proper functioning of the adult retina has just been discovered in vivo by researchers at the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre (CRCHUM). Their study was published in Nature. "For... Continue Reading →
One of the immune system's oldest branches, called complement, may be influencing the severity of COVID disease, according to a new study from researchers at Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Among other findings linking complement to COVID, the researchers found... Continue Reading →
If you've ever wondered why we get goosebumps, you're in good company -- so did Charles Darwin, who mused about them in his writings on evolution. Goosebumps might protect animals with thick fur from the cold, but we humans don't... Continue Reading →
Staring at a deep red light for three minutes a day can significantly improve declining eyesight, finds a new UCL-led study, the first of its kind in humans. Scientists believe the discovery, published in the Journals of Gerontology, could signal the... Continue Reading →
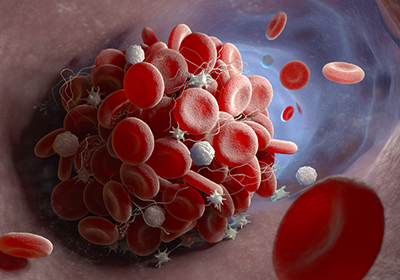
Changes in blood platelets triggered by COVID-19 could contribute to the onset of heart attacks, strokes, and other serious complications in some patients who have the disease, according to University of Utah Health scientists. The researchers found that inflammatory proteins... Continue Reading →
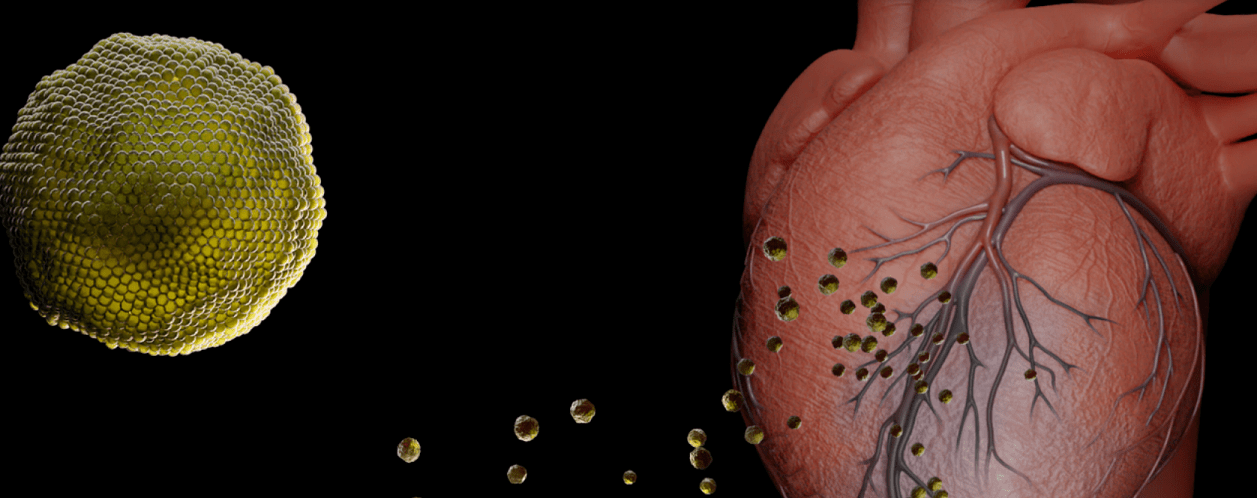
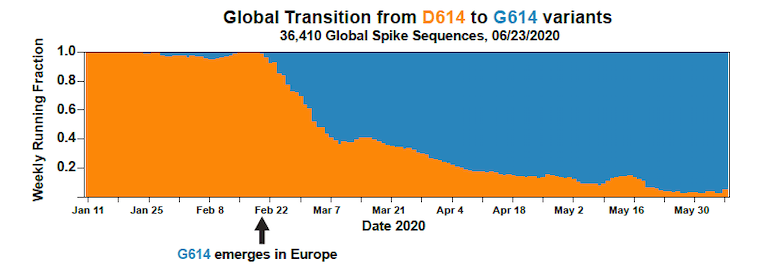
Research out in the journal Cell shows that a specific change in the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus virus genome, previously associated with increased viral transmission and the spread of COVID-19, is more infectious in cell culture. The variant in question, D614G, makes a small... Continue Reading →