As people age, they often lose their motivation to learn new things or engage in everyday activities. In a study of mice, MIT neuroscientists have now identified a brain circuit that is critical for maintaining this kind of motivation. This... Continue Reading →
New research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has revealed that training one arm can improve strength and decrease muscle loss in the other arm -- without even moving it. The findings could help to address the muscle wastage and loss... Continue Reading →
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered a new inflammatory disorder called vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, autoinflammatory and somatic syndrome (VEXAS), which is caused by mutations in the UBA1 gene. VEXAS causes symptoms that included blood clots... Continue Reading →
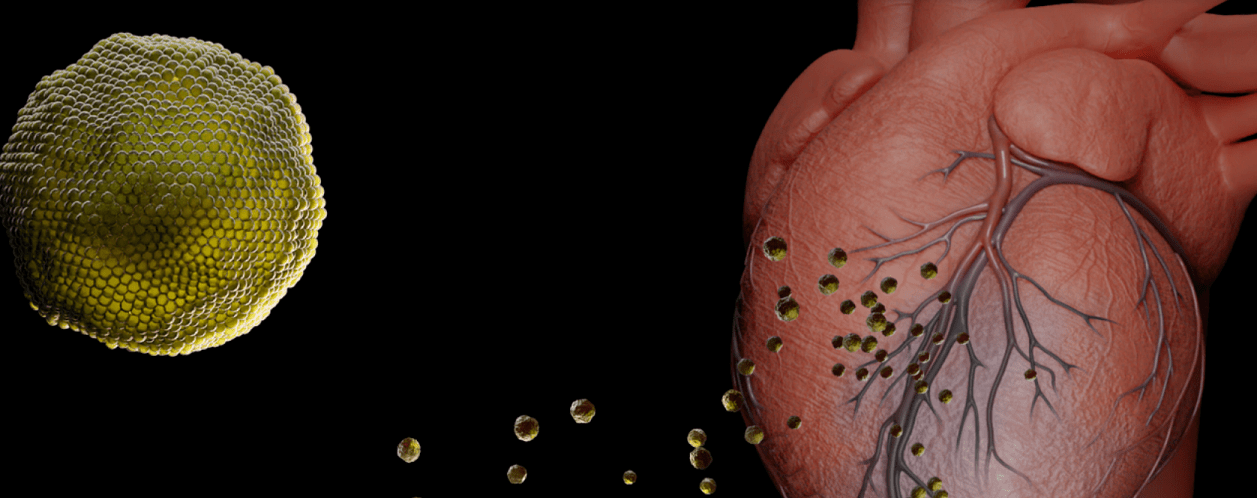
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) -- nanometer sized messengers that travel between cells to deliver cues and cargo -- are promising tools for the next generation of therapies for everything from autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases to cancer and tissue injury. EVs derived... Continue Reading →
Humans are born with a part of the brain that is prewired to be receptive to seeing words and letters, setting the stage at birth for people to learn how to read, a new study suggests. Analyzing brain scans of... Continue Reading →
A McGill-led multi-institutional research team has discovered that during memory consolidation, there are at least two distinct processes taking place in two different brain networks -- the excitatory and inhibitory networks. The excitatory neurons are involved in creating a memory... Continue Reading →
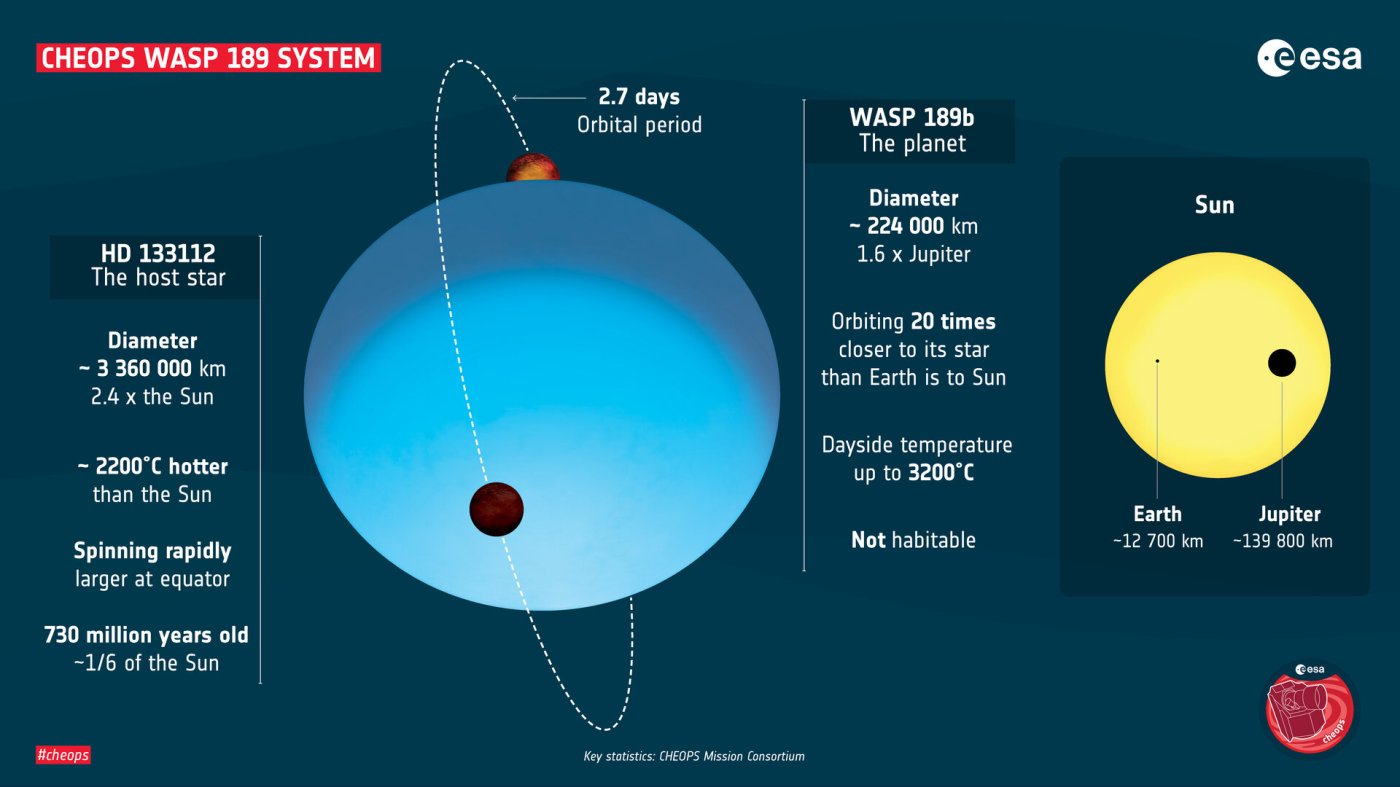
ESA’s new exoplanet mission, Cheops, has found a nearby planetary system to contain one of the hottest and most extreme extra-solar planets known to date: WASP-189 b. The finding, the very first from the mission, demonstrates Cheops’ unique ability to... Continue Reading →
Researchers have developed electronic artificial skin that reacts to pain just like real skin, opening the way to better prosthetics, smarter robotics and non-invasive alternatives to skin grafts. The prototype device developed by a team at RMIT University in Melbourne,... Continue Reading →
Using the venom from 312 honeybees and bumblebees in Perth Western Australia, Ireland and England, Dr Ciara Duffy from the Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research and The University of Western Australia, tested the effect of the venom on the... Continue Reading →